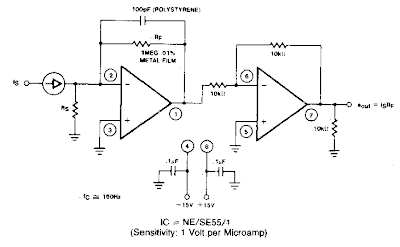
We have already seen in many of my earlier articles how triacs are used in electronic circuits for switching AC loads.
Triacs are basically devices which are able to switch ON a particular connected load in response to an external DC trigger.
Though these may be incorporated for complete switch ON and complete switch OFF procedures of a load, the device is also popularly applied for regulating an AC, such that the output to the load may be reduced to any desired value.
For example triacs are very commonly used dimmer switch applications where the circuit is designed to make the device switch in such a manner that it conducts only for a particular section of the AC sine wave and remains cut OFF during the remaining parts of the sine wave.
This result is an corresponding output AC which has an average RMS value much lower than the actual input AC.
The connected load also responds to this lower value AC and is thus controlled to that particular consumption or resultant output.
This is what exactly happens inside electrical dimmer switches which are normally used for controlling ceiling fan and incandescent lights.
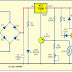
Simple and the Best Triac Dimmer Switch CircuitThe
circuit diagram shown above is an classic example of a dimmer switch, where a triac has been utilized for controlling the intensity of light.
When AC mains is fed to the above circuit, as per the setting of the pot, C2 charges fully after a particular delay providing the necessary firing voltage to the diac.
The diac conducts and triggers the triac into conduction, however this also discharges the capacitor whose charge reduces below the diacs firing voltage.
Due to this the diac stops conducting and so does the triac.
This happens for each cycle of the mains AC sine wave signal, which cuts it into discrete sections, resulting in well tailored lower voltage output.
The setting of the pot sets the charge and the discharge timing of C2 which in turn decides for how long the triac remains in a conducting mode for the AC sine signals.
You might be interested to know why C1 is placed in the circuit, because the circuit would work even without it.
Its true, C1 is actually not required if the connected load is a resistive load like an incandescent lamp etc.
However if the load is an inductive type, the inclusion of C1 becomes very crucial.
Inductive loads have a bad habit of returning a part of the stored energy in the winding, back into the supply rails.
This situation can choke up C2 which then becomes unable to charge properly for initiating the next subsequent triggering.
C1 in this situation helps C2 to maintain is cycle by providing bursts of small voltages even after C2 has completely discharged, and thus maintains the correct switching rate of the triac.
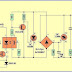
Triac dimmer circuits have the property of generating a lot of RF disturbances in the air while operating and therefore an RC network becomes imperative with these dimmer switches for reducing the RF generations. The above circuit is shown without the feature and therefore will generate a lot of RF which might disturb sophisticated electronic audio systems.
The circuit of a dimmer switch illustrated below incorporate the necessary precautions for subsiding the above issue.